What is STROKE?
The Brain needs Oxygen in order to function properly – just like any other organ in the body. Oxygen is transported within the body through the blood.
Your brain controls a lot of major aspects in the body including muscle movement, speech, sensations (pain, pleasure) and surprisingly – even breathing.
Blockage or injury to the brain’s blood vessels may cause blood rich in oxygen not to get to part of the brain.
If this continues for a long time, the cells in that part of the brain die – leading to a medical condition called Stroke.
Types of stroke
1 A clot may block a blood vessel within the brain, making it difficult for blood to get to a part within the brain. This causes an Ischemic stroke.
2 Bursting of a blood vessel within your brain due to conditions like high blood pressure, weakened arteries and even injuries cause a hemorrhagic stroke.
3 Clots may at times cause temporary blockages on the blood vessels. Symptoms resolve on their own, leading to a Transient Ischemic Attack.
Stroke signs & Symptoms
Watch out for sudden;
- NUMBNESS or weakness of face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
- CONFUSION, trouble speaking or understanding speech.
- TROUBLE SEEING in one or both eyes.
- TROUBLE WALKING, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination.
- SEVERE HEADACHE with no known cause.
If you suspect a stroke, check for the following:
F = Face Drooping – Does one side of the face droop or is it\ numb? Ask the person to smile. Is the person’s smile uneven?
A = Arm Weakness – Is one arm weak or numb? Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
S = Speech Difficulty – Is the person having trouble coordinating their speech?
T = Time to get advanced medical help – Every minute counts. Get help immediately.
Note the time when any of the symptoms first appear.
First aid for STROKE
If you think someone is having a stroke, here is what to do:
- Call emergency services. Stay as calm as possible while waiting for emergency help.
- Make sure they’re in a safe, comfortable position. – Preferably, this should be lying on one side with their head slightly raised and supported in case they vomit.
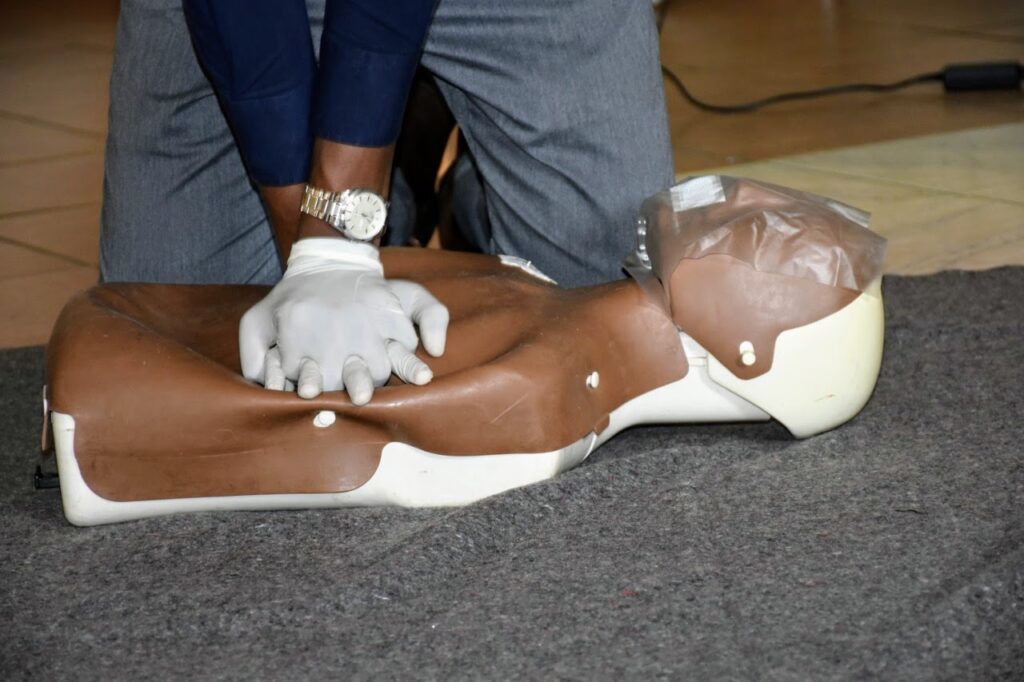
- Check to see if they are breathing.
If they’re not breathing, perform CPR.
🔹If they’re having difficulty breathing, loosen any constrictive clothing, such as a tie or scarf.
4 Cover with a blanket to keep them warm.
Do not give them anything to eat or drink.
🔹 If the person is showing any body weakness, avoid moving them.
🔹 Observe the person carefully for any change in condition – Note the time that their symptoms started.
Long term stroke management
Long-term stroke management is aimed at preventing another stroke and minimizing the effects of the stroke that has already occurred. It is important to work with a healthcare team that includes a stroke neurologist, a rehabilitation specialist, and a primary care physician.
The goals of long-term stroke management include:
Some of the medications that may be used to prevent another stroke include:
· Antiplatelet drugs: These drugs help to prevent blood clots from forming. Examples of antiplatelet drugs include aspirin and clopidogrel.
· Anticoagulants: These drugs help to keep the blood flowing smoothly. Examples of anticoagulants include warfarin and rivaroxaban.
· Statins: These drugs help to lower cholesterol. High cholesterol is a risk factor for stroke.
Lifestyle changes include:
· Quitting smoking: Smoking increases the risk of stroke.
· Eating a healthy diet: A healthy diet can help to control blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar.
· Exercising regularly: Exercise can help to improve overall health and reduce the risk of stroke.
· Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity is a risk factor for stroke.
Rehabilitation services that can help people who have had a stroke to regain their independence include:
· Physical therapy: Physical therapy to help improve their mobility and strength.
· Occupational therapy: Occupational therapy to help improve ability to perform activities of daily living such as dressing, bathing, and eating.
· Speech therapy: Speech therapy can help people to improve their communication skills.
Long-term stroke management can be challenging, but there are many resources available to help make a difference in recovery.
Emergency Contacts: 1514 (Red Cross), 0714911911(Rescue), 0721225285 (St. John), 0725225225 (AAR), 0730811000(AMREF).